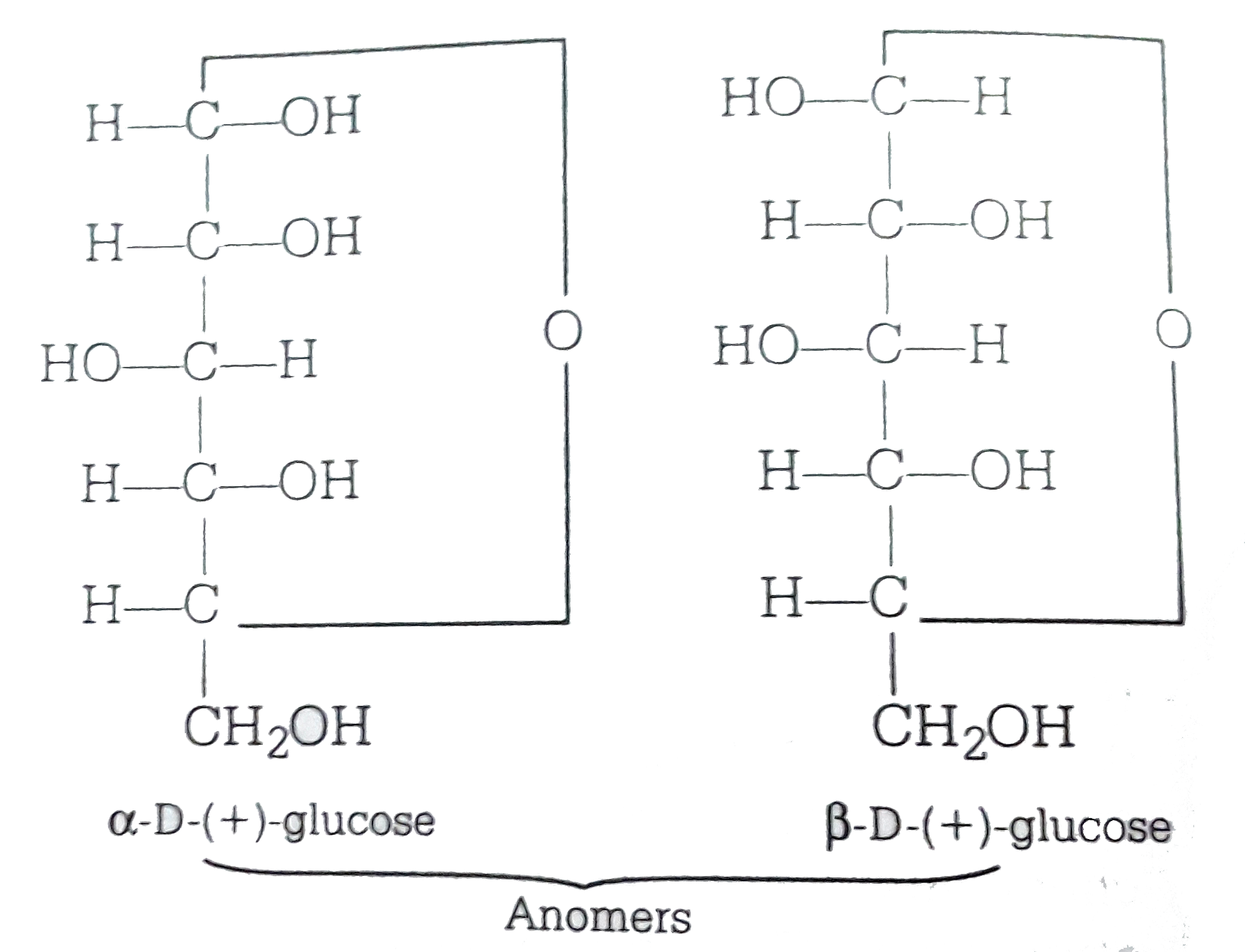
Alpha D Glucose and Beta D Glucose Are Enantiomers
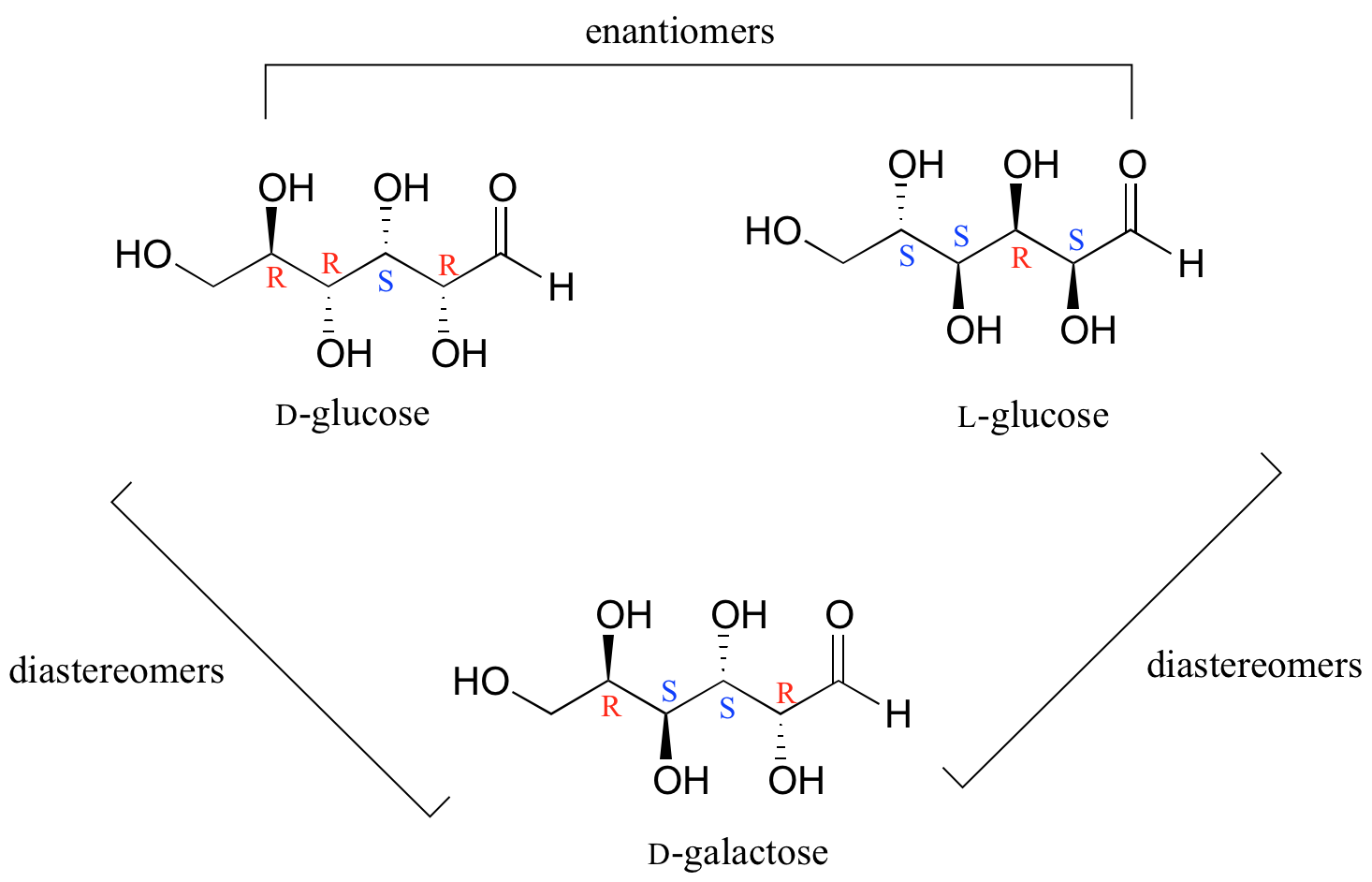
There are two enantiomers of glucose, called D-glucose and L-glucose. The D-enantiomer is the common sugar that our bodies use for energy. It has n = 4 stereocenters, so therefore there are 2 n = 2 4 = 16 possible stereoisomers (including D-glucose itself). In L-glucose, all of the stereocenters are inverted relative to D-glucose. That leaves.

Enantiomers vs Diastereomers What are Enantiomers? Video & Lesson Transcript
Q1 What are Epimers with examples? Epimers are carbohydrates that differ in the location of the -OH group in one location. Both D-glucose and D-galactose are the best examples. D-glucose and D-galactose epimers create a single difference at C-4 carbon. They are not enantiomers, they are just epimers, or diastereomers, or isomers. Q2

Enantiomers Of Alpha D Glucose Johnathon Howells
Enantiomers of glucose. The enantiomer of lactic Acid. Nomenclature for enantiomers. The absolute configuration of enantiomers can be explained by using: D/L nomenclature system; R/S nomenclature system; D/L system. Although D/L is an old system of nomenclature but still most widely used for amino acids and carbohydrates. In order to determine.
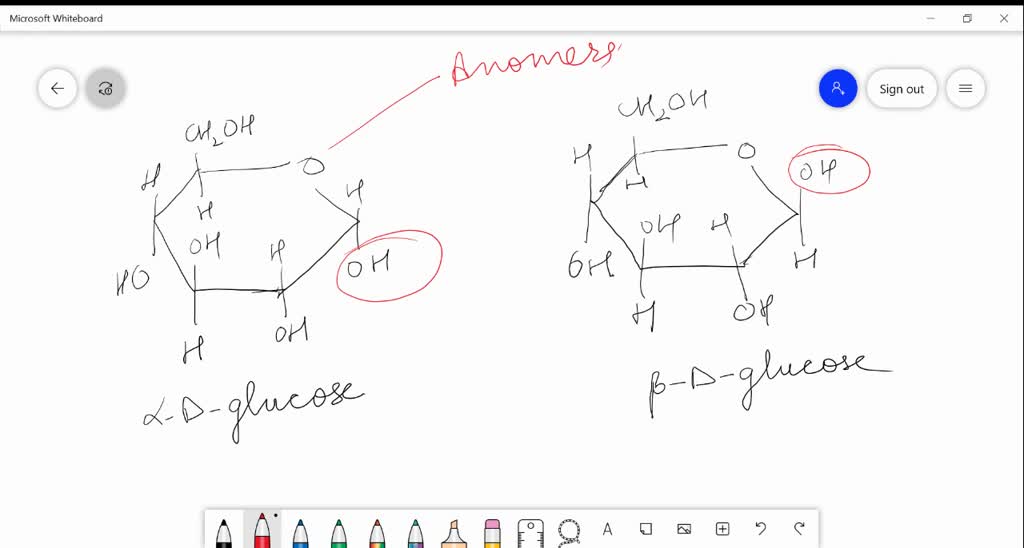
SOLVEDαDglucose and βDglucose are (a) anomers (b) C2 epimers (c) C3 epimers (d) enantiomers
D- and L-is an old but still-convenient shorthand for saying that molecules are enantiomers. e.g. D-glucose and L-glucose are non-superimposable mirror images without having to write out a long IUPAC name with lots of ( R) and ( S) descriptors. Most natural sugars are D- and most natural amino acids are L- .
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chirality-diagram-56a12ca45f9b58b7d0bcc7b5.png)
What is an Enantiomer?
Their enantiomers were given the same name with the introduction of systematic nomenclatures, taking into account absolute stereochemistry (e.g. Fischer nomenclature, d / l nomenclature). For the discovery of the metabolism of glucose Otto Meyerhof received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1922. [16]

CH103 Chapter 6 Natural Products and Organic Chemistry Chemistry
Although sugar enantiomers may display the same or similar biological activity, it is obvious that the protein-binding properties of a d -sugar component of a lead synthetic glycoside are different from its L-enantiomer (or vice versa).

Adisi Nukleofilik
The D-enantiomer is the common sugar that our bodies use for energy. It has n = 4 stereocenters, so therefore there are 2 n = 2 4 = 16 possible stereoisomers (including D-glucose itself). In L-glucose, all of the stereocenters are inverted relative to D-glucose. That leaves 14 diastereomers of D-glucose: these are molecules in which at least.

Enantiomers in nature CheMystery
There are two enantiomers of glucose, called D-glucose and L-glucose. The D-enantiomer is the common sugar that our bodies use for energy. It has n = 4 stereocenters, so therefore there are 2 n = 2 4 = 16 possible stereoisomers (including D-glucose itself). In L-glucose, all of the stereocenters are inverted relative to D-glucose. That leaves.
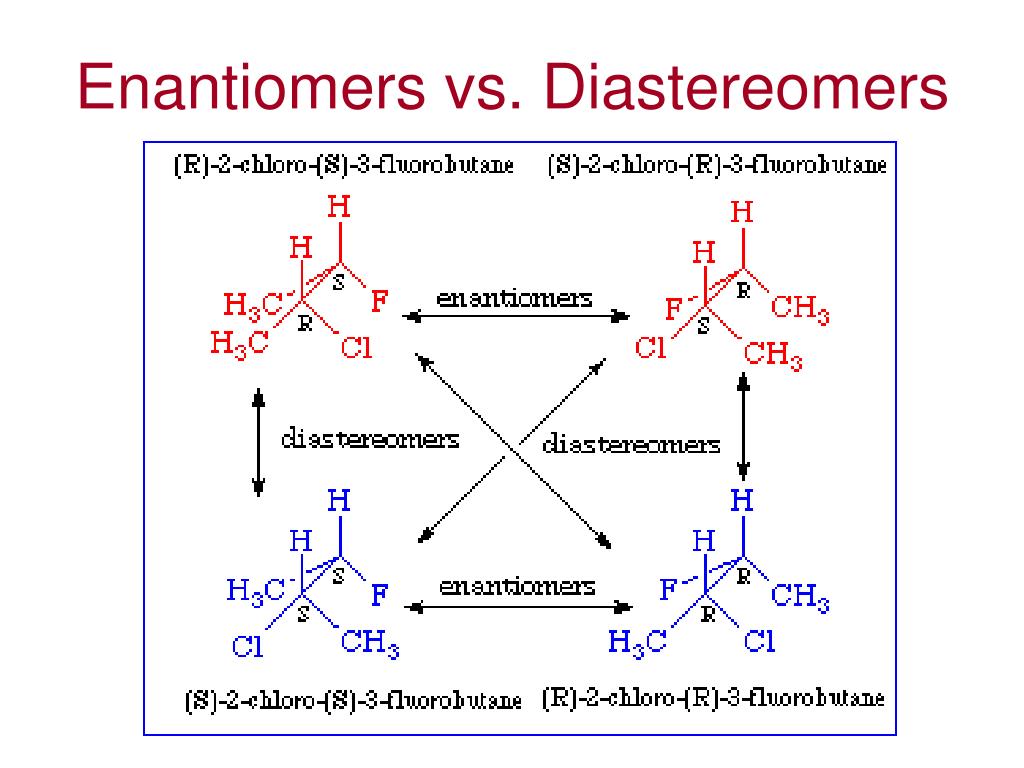
PPT Isomerism Recap PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID397852
Thus, L-glucose and D-glucose are enantiomers, but D-Erythrose and D-Threose are diastereomers. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Diastereomers. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): Enantiomers. Sugars of 5-7 carbons can fairly easily form ring structures (called Haworth structures). For aldoses like glucose, this involves formation of a hemi-acetal.
Chiral responsive CdotsAu NP complex towards glucose enantiomers. (a)... Download Scientific
The confusion about D and L arises because the L sugars of a given name (glucose, for example) are mirror images of the D sugars of the same name. This concept is most easily seen with glyceraldehyde. In the same way D- and L- glyceraldehyde represent two enantiomers, the D- and L- forms larger monosaccharides are enantiomers of one another.
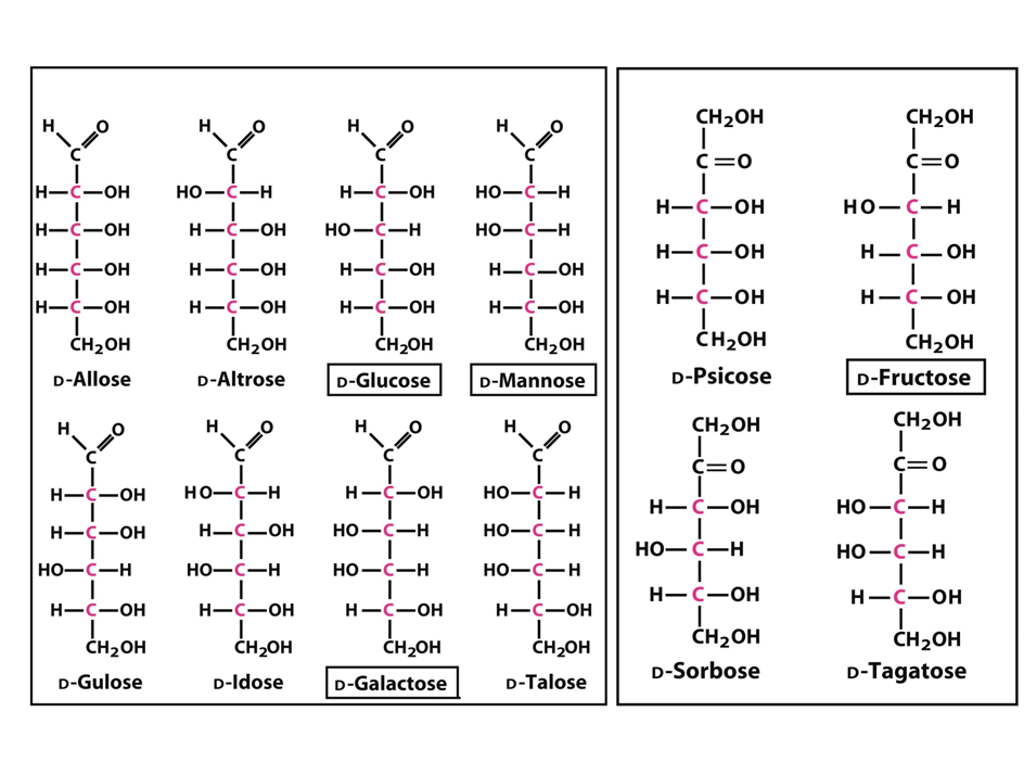
Solved CH2OH CH2OH HCOH HCOH HCOH CH2OH DAltrose
For example, let's consider the glucose molecule in its open-chain form (recall that many sugar molecules can exist in either an open-chain or a cyclic form). There are two enantiomers of glucose, called D-glucose and L-glucose. The D-enantiomer is the common sugar that our bodies use for energy. It has n = 4 stereocenters, so therefore.
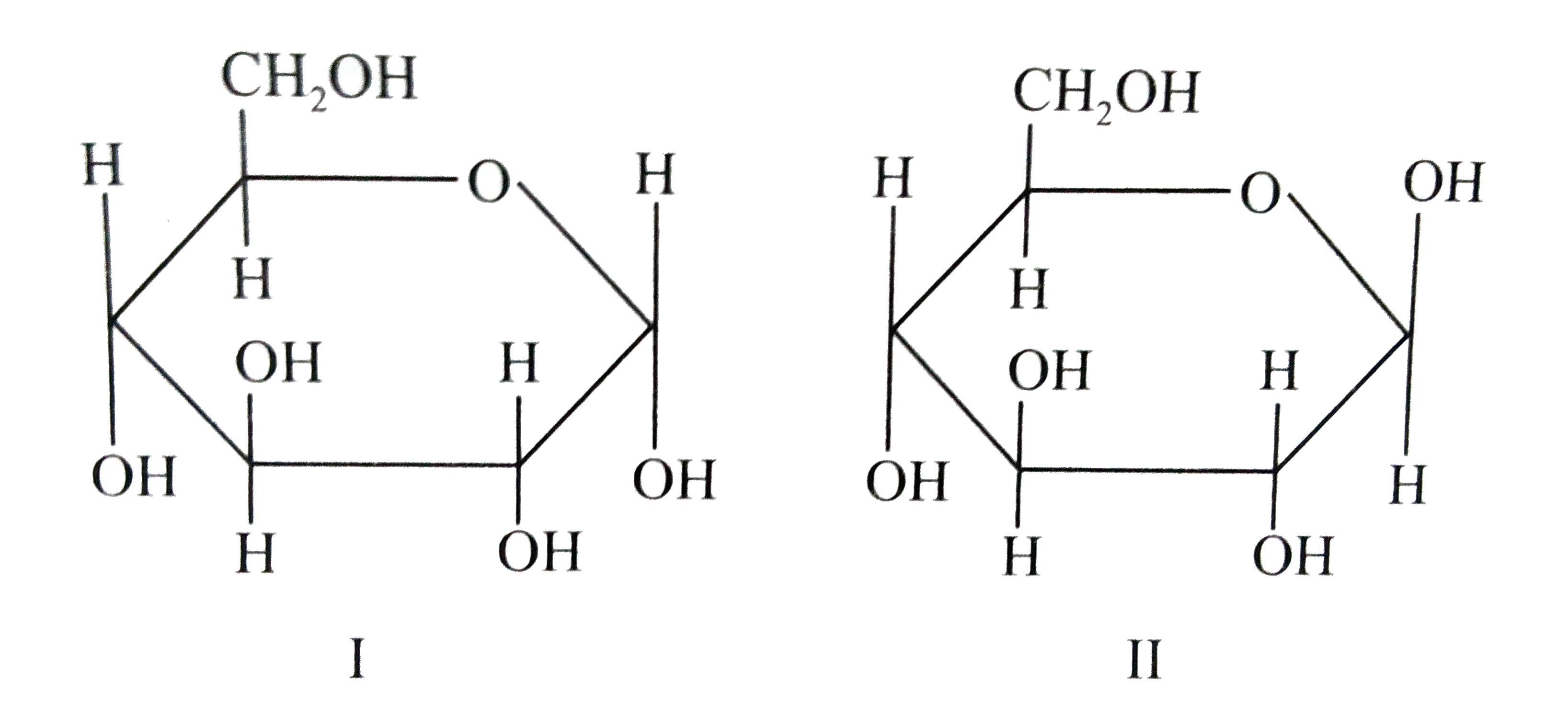
Alpha D Glucose and Beta D Glucose Are Enantiomers
Enantiomers are a pair of molecules that exist in two forms that can not be superimposed on each other but are mirror images of each other. They have a chiral carbon which is a center of carbon.

Solved (D) and (L) glucose are enantiomers. (D) gallose is a
The Epimers of glucose involve some formations, some examples are starch, glycogen, glucose, polysaccharides, and oligosaccharides. The stereoisomers β-D-mannopyranose and β-D-glucopyranose are known as epimers because they differ only in the C-2 position of stereochemistry. The hydroxyl group in the β-D-glucopyranose molecule is equatorial.
5.8 Diastereomers Chemistry LibreTexts
The D- and L-glucose are true enantiomers. So, enantiomers, which means that they're complete mirror images. They differ at every single chiral carbon. Now that being said, if the D-aldohexoses, these glucose, if the D- and L-aldohexoses are enantiomers, that means that all of the D-aldohexoses have to be diastereomers of each other, because.

Epimers and Anomers Chemistry Steps
There are two enantiomers of glucose, called D-glucose and L-glucose. The D-enantiomer is the common sugar that our bodies use for energy. It has n = 4 stereocenters, so therefore there are 2 n = 2 4 = 16 possible stereoisomers (including D-glucose itself). In L-glucose, all of the stereocenters are inverted relative to D-glucose. That leaves.
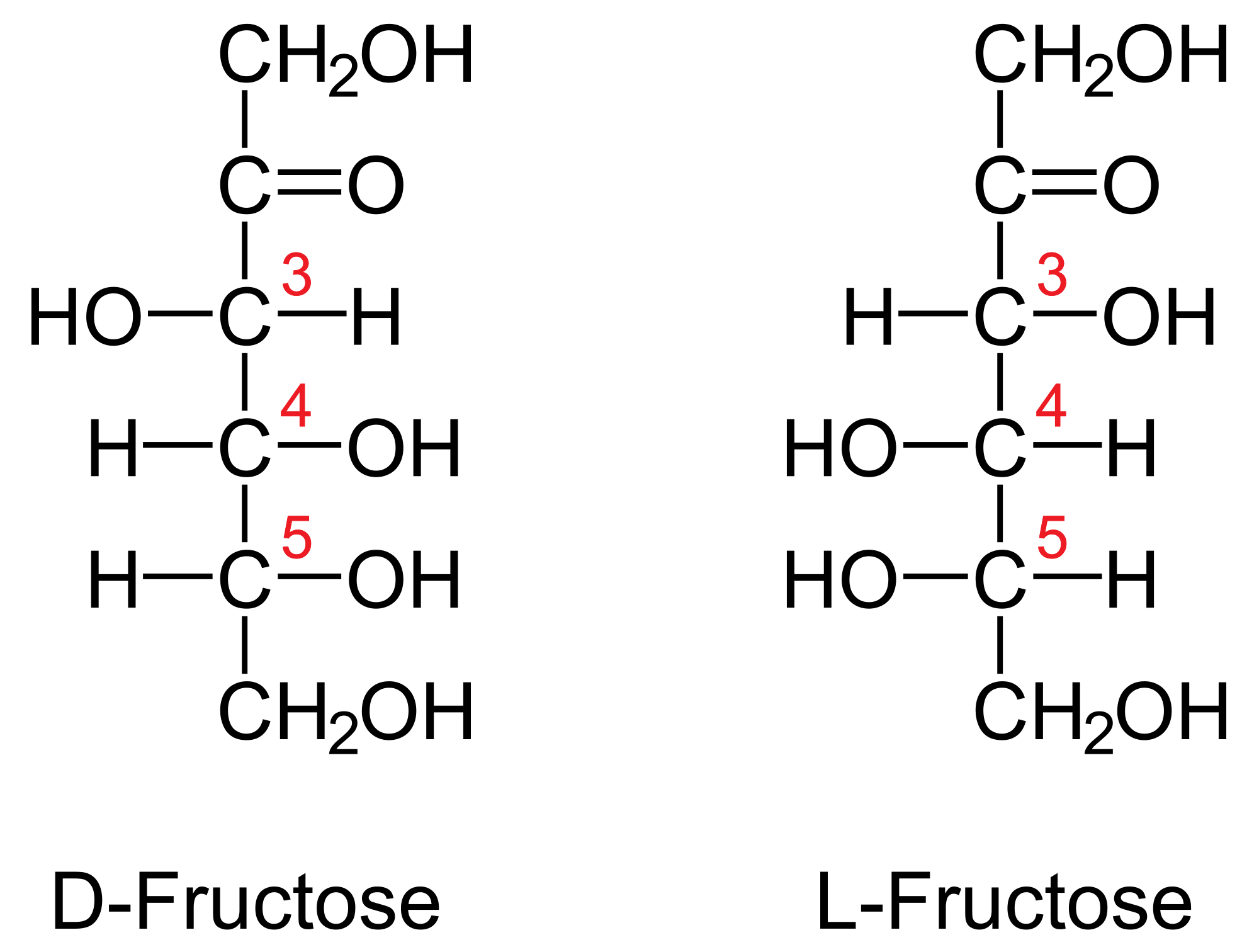
Glucose And Fructose
Enzyme-free substrate is used for SERS sensing glucose enantiomers. • Au NPs play as the oxidase mimics instead of the SERS substrate. • Intrinsic structure of MOFs is favorable for applying as nanoreactors. • Enantioselective identification is achieved via onsite growth of Prussian blue. • This platform is also useful for other.